As people commemorate the Fourth of July, eye experts at Vanderbilt University Medical Center urge caution when handling fireworks.
“While fireworks can be enjoyable to watch, they can be extremely dangerous,” said Sylvia Groth, MD, associate professor of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences at Vanderbilt Eye Institute. “We just want to remind people that you can experience devastating vision loss if you are not properly handling fireworks.”
Injuries range from chemical burns with cornea involvement, lid lacerations, orbital floor fractures (blowout fractures) and ruptured globes (meaning the eye was cut open).
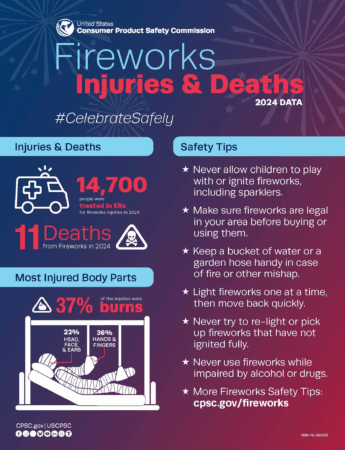
Groth recalled that one recent year, in a single shift, she and her team treated 11 firework injuries at Vanderbilt and Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt. The majority were children.
“We are not talking about a bit of singeing of eyelashes,” she stressed. “We treated injuries from projectile fireworks. These patients will be forever impacted by their injuries.”
Many think sparklers are a safe alternative, but they are responsible for most injuries from fireworks in children 5 years old and younger. Sparklers burn at about 2,000 degrees — hot enough to melt some metals — and can quickly ignite clothing and cause severe burns to the face, hands and feet.
Researcher Tonia Rex, PhD, professor of Ophthalmology & Visual Sciences at VUMC who studies trauma-induced vision loss, said to consider the percentage of space the eye takes up on the body.
“It’s really a pretty small area,” said Rex. “But if you look at the percentage of burns that are incurred from fireworks that impact the eyes, it’s 14%. Typically, these injuries, which occur to the head, face, ears, make up 21% of injuries, and it’s usually because a person is looking right at the firework, or their eyes are in direct danger as they play with sparklers.
“Sparklers are a flammable object, and when children are swinging them around or using them as swords with their friends, the sparker can fly off and cause serious injury.”
Groth, who treats patients, said injuries range from chemical burns with cornea involvement, lid lacerations, orbital floor fractures (blowout fractures) and ruptured globes (meaning the eye was cut open).
Both Groth and Rex stress that protective goggles or clear, shatter-proof protective glasses are recommended when handling fireworks.
The National Safety Council offers the following tips:
- Never allow young children to handle fireworks.
- Anyone using fireworks or standing nearby should wear protective eyewear.
- Never hold lighted fireworks in your hands.
- Only use them away from people, houses and flammable material.
- Only light one firework at a time, and maintain a safe distance after lighting.
- Do not try to re-light or handle malfunctioning fireworks.
- Soak both spent and unused fireworks in water for a few hours before discarding.
- Keep a bucket of water nearby to fully extinguish fireworks that don’t go off, or in case of fire.